Which Of The Choices Best Describe Website Host Services? Check All Of The Boxes That Apply.
A server is a estimator program or device that provides a service to another computer plan and its user, as well known as the client. In a data center, the physical computer that a server program runs on is also frequently referred to as a server. That machine might exist a defended server or information technology might be used for other purposes.
In the customer/server programming model, a server program awaits and fulfills requests from client programs, which might be running in the same, or other computers. A given application in a computer might role every bit a client with requests for services from other programs and as a server of requests from other programs.
How servers work
The term server can refer to a concrete machine, a virtual auto or to software that is performing server services. The way that a server works varies considerably depending on how the discussion server is existence used.
Physical and virtual servers
A physical server is simply a reckoner that is used to run server software. The differences between a server and a desktop calculator will exist discussed in detail in the next section.
A virtual server is a virtual representation of a physical server. Similar a physical server, a virtual server includes its ain operating system and applications. These are kept separate from whatever other virtual servers that might be running on the physical server.
The process of creating virtual machines involves installing a lightweight software component called a hypervisor onto a physical server. The hypervisor's job is to enable the physical server to function every bit a virtualization host. The virtualization host makes the physical server's hardware resources -- such as CPU time, retention, storage and network bandwidth -- available to ane or more virtual machines.
An authoritative panel gives administrators the ability to allocate specific hardware resources to each virtual server. This helps dramatically drive down hardware costs considering a single physical server tin run multiple virtual servers, as opposed to each workload needing its ain physical server.
Server software
At a minimum, a server requires two software components: an operating system and an application. The operating system acts every bit a platform for running the server application. It provides access to the underlying hardware resource and provides the dependency services that the application depends on.
The operating system too provides the means for clients to communicate with the server application. The server'due south IP address and fully qualified domain name, for example, are assigned at the operating system level.
Desktop computers vs. servers
At that place are both similarities and differences between desktop computers and servers. Most servers are based on X86/X64 CPUs and tin can run the same code as an X86/X64 desktop computer. Unlike most desktop computers, however, physical servers often include multiple CPU sockets and error correcting memory. Servers besides by and large support a far greater quantity of retention than most desktop computers.
Because server hardware typically runs mission-disquisitional workloads, server hardware manufacturers blueprint servers to back up redundant components. A server might be equipped with redundant power supplies and redundant network interfaces. These redundant components allow a server to keep to role even if a key component fails.
Server hardware also differs from desktop hardware in terms of its form factor. Modern desktop computers often exist as mini towers, designed to exist placed under a desk. Although there are still some vendors that offer tower servers, about servers are designed to be rack mounted. These rack mountain systems are described as having a 1U, 2U or 4U course factor, depending on how much rack space they occupy -- a 2U server takes up twice as much rack infinite as a 1U server.

Another key difference between a desktop reckoner and a server is the operating system. A desktop operating arrangement might be able to perform some server-like functionality but isn't designed or licensed to take the identify of a server operating system. Windows 10, for example, is a desktop operating system.
Some Windows x editions include Hyper-V, Microsoft's virtual machine platform. Even though both Windows 10 and Windows Server can run Hyper-5, Windows 10's hypervisor is intended to be primarily used for development purposes, whereas the version of Hyper-Five included with Windows Server is designed for running production virtual servers.
Although an organisation could conceivably run a virtual server on top of Windows 10 Hyper-V, there are licensing issues to consider. Additionally, Windows Server Hyper-V includes resiliency features that aren't found in the Windows ten version. For case, Windows Server supports failover clustering and virtual machine replication.
Similarly, the Windows 10 operating system tin can make files available to devices on a local network. However, Windows x was never designed for large-scale file sharing. Windows Server, however, tin can be configured to act as a fully featured file server. In large organizations, a distributed file system can be created across an unabridged server farm for the purpose of providing better performance, scalability and resiliency than what 1 physical server would be able to provide by itself.
Types of servers
Servers are often categorized in terms of their purpose. A few examples of the types of servers bachelor are as follows:
- Web server: a calculator program that serves requested HTML pages or files. In this case, a spider web browser acts as the client.
- Awarding server: a programme in a calculator in a distributed network that provides the business organization logic for an application program.
- Proxy server: software that acts as an intermediary betwixt an endpoint device, such as a computer, and some other server from which a user or customer is requesting a service.
- Mail server: an application that receives incoming emails from local users -- people within the same domain -- and remote senders and forwards approachable emails for delivery.
- Virtual server: a program running on a shared server that is configured in such a manner that it seems to each user that they have complete control of a server.
- Blade server: a server chassis housing multiple thin, modular electronic circuit boards, known equally server blades. Each blade is a server in its ain right, oftentimes dedicated to a unmarried awarding
- File server: a estimator responsible for the primal storage and management of data files so that other computers on the aforementioned network can access them.
- Policy server: a security component of a policy-based network that provides potency services and facilitates tracking and command of files.
- Database server: this server is responsible for hosting one or more databases. Client applications perform database queries that recall data from or write data to the database that is hosted on the server.
- Impress server: this server provides users with access to one or more network-attached printers -- or print devices equally some server vendors call them. The print server acts every bit a queue for the print jobs that users submit. Some impress servers can prioritize the jobs in the print queue based on the job type or on who submitted the impress job.
Server components
Hardware
Servers are fabricated up of several unlike components and subcomponents. At the hardware level, servers are typically made upwards of a rack mount chassis containing a power supply, a arrangement lath, one or more CPUs, retention, storage, a network interface and a power supply.
About server hardware supports out-of-band management through a defended network port. Out-of-band management enables depression-level management and monitoring of the server, independently of the operating organization. Out-of-band management systems can exist used to remotely power the server on or off, to install an operating system, and to perform health monitoring.
Operating systems
Another component is the server operating organization. A server operating system, such as Windows Server or Linux, acts every bit the platform that enables applications to run. The operating system provides applications access to the hardware resource that they need and enables network connectivity.
The application is what enables the server to practise its job. For instance, a database server would run a database application. Likewise, an electronic mail server would need to run a mail service application.
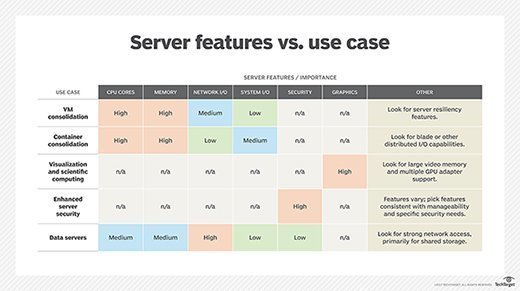
Choosing the right server
There are many factors to consider in the midst of a server selection, including virtual auto and container consolidation. When choosing a server, evaluate the importance of sure features based on the use cases.
Security capabilities are also important and there are a number of protection, detection and recovery features to consider, including native data encryption to protect data in flight and data at residue, as well as persistent event logging to provide an indelible tape of all activity.
If the server will rely on internal storage, the selection of disk types and capacity is also important because it can take a significant influence on input/output (I/O) and resilience.
Many organizations are shrinking the number of physical servers in their data centers as virtualization enables fewer servers to host more workloads. The advent of cloud computing has also changed the number of servers an organization needs to host on premises.
Packing more capability into fewer boxes tin can reduce overall capital expenses, information eye floor space and power and cooling demands. Hosting more workloads on fewer boxes, however, can too pose an increased risk to the business organisation because more workloads will exist afflicted if the server fails or needs to be offline for routine maintenance.
A server maintenance checklist should cover physical elements, also as the arrangement'south disquisitional configuration.

Download a PDF of this server maintenance checklist.
Which Of The Choices Best Describe Website Host Services? Check All Of The Boxes That Apply.,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/server
Posted by: pridgentwitir.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Choices Best Describe Website Host Services? Check All Of The Boxes That Apply."
Post a Comment